Table of Contents
Why Are Cable Glands Used? Your Guide to Safe and Secure Cables
(Keep Reading! This Guide Makes it Easy!)
H1: Why Cable Glands Are Used: Keeping Things Safe and Working Right
Have you ever seen wires going into a box or machine? How do they stay put? How do they stay safe from rain or dust? That’s where cable glands come in!
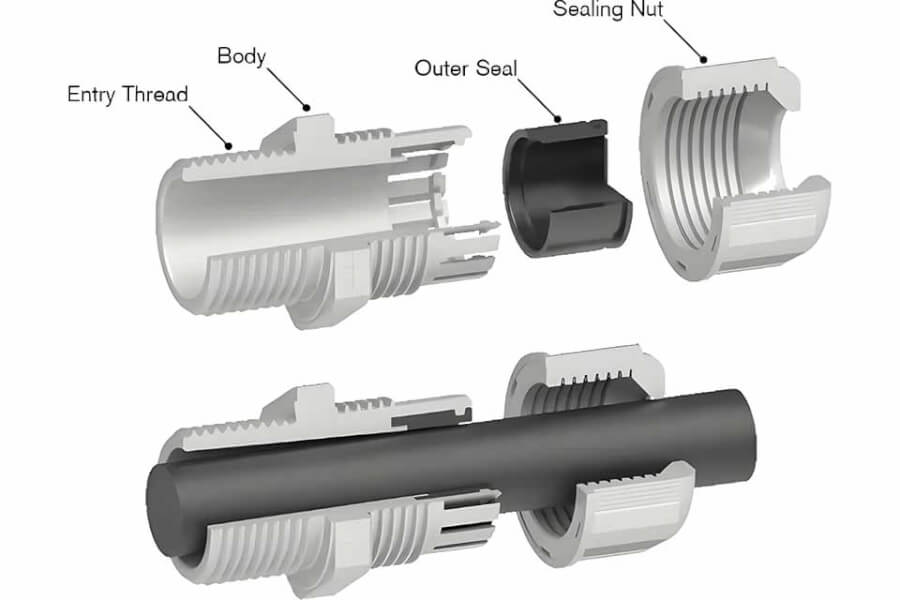
Imagine a tiny door for your wires. A cable gland is like a special, strong door that holds the wire tight where it enters a piece of equipment. It stops the wire from being pulled out. It also seals the hole. This keeps bad stuff like water and dirt away from the important parts inside.
Problem: Wires need to go into machines, boxes, and buildings. But just drilling a hole is not safe.
- Water can get in and break things.
- Dust can clog up moving parts.
- The wire could get pulled out or damaged.
- In some places, a spark could cause a big fire or explosion!
Agitate: Think about when your phone gets wet. It stops working, right? Imagine that happening to a big, costly machine in a factory! Water or dust getting inside electrical boxes is a huge headache. It causes breakdowns. Work stops. Money is lost. Worse, loose or damaged wires can cause shocks or fires. People could get hurt. In places like oil rigs or mines, a tiny spark from a bad connection could be a disaster. It’s scary to think about! Fixing these problems costs a lot of time and money. Sometimes, you might even get fined if you don’t follow safety rules.
Solution: Using the right cable gland solves these big problems! They are small parts, but they do a very important job. They make sure wires are held tight and safe. They seal the entry point completely. This keeps everything inside protected and working the way it should.
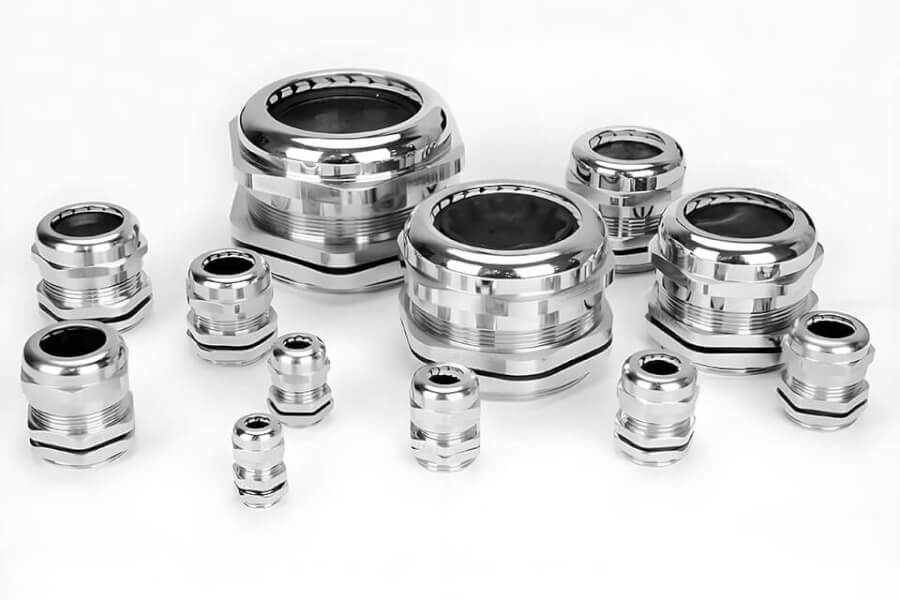
We are a cable gland manufacturer based in China. We make many kinds of cable glands to help you. We make strong plastic water proof cable gland. We make tough metal water proof cable gland. We even make special multi hole cable gland for lots of wires. We also make junction box options to keep wire connections safe. We know how important safety is. Our products are made to solve your cable problems reliably.
This guide will show you exactly why cable glands are used and why they are so vital.
H2: 7 Big Reasons Cable Glands Are So Important
Cable glands might seem small. But they do many big jobs. Let’s look at the 7 main reasons they are needed everywhere.
1. Keeping Bad Stuff Out (Environmental Protection)
Problem: Electrical things don’t like water, dust, dirt, or yucky chemicals. These things can sneak into equipment through the holes made for cables.
Agitate: If water gets into an electrical box outside, zap! It can short circuit. Everything stops working. Dust in a factory can build up inside machines. They can overheat or break down. Chemicals in the air at some plants can eat away at wires and connections. This damage costs a lot to fix. It can stop work for days! Think about boats or things near the sea. Saltwater is very bad for metal parts if they aren’t protected.
Solution: Cable glands act like super seals! They clamp around the cable. They seal the hole tight. Good cable glands have special ratings, like IP68. This means they are really good at stopping dust and water, even if they go underwater for a while!
- They stop rain, splashes, and even jets of water.
- They keep out fine dust in workshops or deserts.
- Special ones resist oils and chemicals in factories.
- IP68 cable glands for marine use are great near the ocean because they fight salt corrosion.
As a cable gland manufacturer in China, we make high-quality plastic water proof cable gland and metal water proof cable gland options. These have excellent IP ratings. They give you peace of mind that your equipment is sealed and safe from the environment. Our metal glands, often made of brass or stainless steel, are super tough against corrosion.
2. Holding Cables Tight (Mechanical Safety and Strain Relief)
Problem: Cables can get pulled or twisted. Machines often vibrate or move. If the cable is loose where it enters a box, it can get damaged easily.
Agitate: Imagine a wire getting yanked hard. The connection inside could break. The machine stops. Or think about a wire connected to a motor that shakes a lot. Over time, the shaking can wear out the wire’s protective cover right where it enters the box. This can lead to bare wires showing – very dangerous! If a cable just hangs loose, its own weight can put stress on the connection point. This constant pulling is called “strain.” Too much strain leads to failure. Replacing damaged cables takes time and stops production.
Solution: Cable glands provide strain relief. This means they grip the cable firmly before it goes into the sensitive connection area.
- They prevent the cable from being pulled out accidentally.
- They stop twists and bends right at the entry point.
- They absorb vibrations so the connection inside isn’t shaken apart.
This makes the whole setup much stronger and safer. The cable lasts longer. The machine keeps running. We manufacture cable glands designed for strong grip and excellent strain relief. Whether you need a simple plastic gland for a control panel or a robust metal gland for heavy machinery, we ensure our products hold your cables securely. This mechanical safety is a core function.
3. Safety in Dangerous Places (Hazardous Area Compliance)
Problem: Some places have gas or dust in the air that can easily catch fire or explode. Think about oil refineries, gas stations, mines, or chemical plants. Electrical equipment in these places needs special protection.
Agitate: A tiny spark from a loose wire or a normal electrical switch can be catastrophic in these “hazardous areas.” An explosion could destroy equipment, cause massive fires, and badly injure people. The costs are huge – repairs, lost production, legal issues, and most importantly, the risk to human life. You cannot just use any electrical part in these zones. There are very strict safety rules and laws (like ATEX in Europe or IECEx internationally). Not following them leads to big trouble.
Solution: Special explosion-proof cable glands are made for these dangerous places. They are built incredibly strong.
- They contain any spark or explosion inside the electrical box, stopping it from igniting the outside air. This is called “flameproof.”
- They seal perfectly to prevent flammable gas or dust from getting inside.
- They often have extra grounding features for added safety.
- They must pass tough tests to get certifications like ATEX-certified cable glands or IECEx.
Using certified explosion-proof cable glands is not optional in hazardous areas; it’s required by law for safety. We understand the critical need for safety in these environments. While our main focus is on waterproof glands, we recognize the importance of explosion-proof cable glands and can guide customers needing these specialized solutions for oil & gas or mining applications. Ensuring you use the right certified gland is key to preventing disaster.
4. Keeping Electricity Flowing Right (Electrical Continuity and Grounding)
Problem: Some cables have a metal layer inside, like armor, for extra protection. This metal armor needs to be connected properly to the earth (ground) for safety. Also, sometimes electrical “noise” (interference) can mess up signals in sensitive data cables.
Agitate: If the metal armor isn’t grounded correctly, it could become live with electricity if there’s a fault! Anyone touching the equipment could get a serious shock. It’s a hidden danger. Electrical noise, called EMI or RFI, is like static on a radio. It can garble computer data or mess up control signals in a factory. This can lead to errors, slowdowns, or equipment behaving strangely.
Solution: Many cable glands, especially metal ones, help solve these problems.
- They provide electrical continuity. This means they make a good electrical connection between the cable’s metal armor and the metal box the cable enters.
- This connection safely grounds the armor, carrying away any dangerous stray electricity.
- Some metal glands also help shield against EMI/RFI noise, keeping signals clean, especially for data centers or telecom gear.
Choosing a metal water proof cable gland made from materials like brass often ensures good grounding. This is vital for safety with armored cables. We ensure our metal glands provide reliable connections for grounding needs, helping protect both people and sensitive equipment.
5. Making Cables Last Longer (Cable Longevity and Maintenance Reduction)
Problem: Cables are often exposed to harsh conditions. Sunlight, chemicals, rubbing, bending, and constant vibration can wear them out over time.

Agitate: Replacing cables is a pain! It costs money for the new cable and for the worker’s time. Often, the equipment has to be shut down during the replacement, meaning lost production time. If a cable fails unexpectedly, it can cause sudden breakdowns at the worst possible moment. Frequent replacements add up to significant costs and hassle over the life of a machine or installation.
Solution: Cable glands help protect the cable right where it’s most vulnerable – the entry point.
- They seal out damaging elements like UV light, moisture, and chemicals that degrade cable jackets.
- They prevent sharp bends that can break the wires inside.
- They reduce wear from vibration by holding the cable steady.
- They stop abrasion (rubbing) against the edge of the entry hole.
By providing this protection, a good cable gland significantly increases the cable longevity. This means fewer replacements, less downtime, and lower maintenance costs over time. Our plastic and metal cable glands are designed for durability. They help shield your cables, contributing to a more reliable and cost-effective operation. Investing in quality glands saves money in the long run.
6. Meeting the Rules (Compliance with Industry Standards)
Problem: Many industries have specific rules and safety standards for electrical installations. These rules often require proper cable management, including the use of appropriate cable glands.
Agitate: If your electrical work doesn’t meet the required standards (like NFPA 70 in the US, IEC standards internationally, or DNV for marine), you could fail inspections. This might mean you have to redo the work, costing time and money. Your insurance might be affected. In regulated industries like energy, construction, or aerospace, non-compliance can lead to fines or even legal action. You might not be allowed to operate until the issues are fixed.
Solution: Using the correct type of cable gland is often essential for meeting these standards.
- Standards often specify minimum IP ratings for sealing against dust and water.
- Rules for hazardous areas demand certified explosion-proof cable glands.
- Requirements for strain relief ensure cables aren’t damaged by pulling.
- Grounding requirements for armored cable often necessitate specific metal glands.
By using compliant cable glands, you ensure your installation meets safety codes and passes inspections. This keeps your projects on track and avoids penalties. As a cable gland manufacturer, we produce glands that meet common international standards for sealing and performance. We provide the specifications you need (like IP ratings) to help you choose the right product for compliance in your industry.
7. Working with All Kinds of Cables (Versatility Across Cable Types)
Problem: There isn’t just one type of electrical cable. There are many! Some are thick, some are thin. Some have metal armor (armored cable), some don’t (non-armored cable). Some are round, some are flat. How do you secure all these different types?
Agitate: Using the wrong device to secure a cable is asking for trouble. A clamp too big won’t seal properly, letting in dirt and water. A clamp too small might damage the cable or just not fit. Trying to force a gland meant for a round cable onto a flat one won’t work well. It could leave gaps or crush the cable. This leads to all the problems we talked about: poor sealing, no strain relief, and potential damage.
Solution: Cable glands are designed to be versatile! They come in many shapes, sizes, and materials to fit different needs.
- There are specific glands designed for armored cables (like SWA – Steel Wire Armored) that include features to clamp and ground the armor.
- There are simpler, effective glands for non-armored cables.
- They come in a huge range of sizes to match different cable diameters.
- Materials like nylon (plastic), brass, and stainless steel offer different benefits (cost, corrosion resistance, strength).
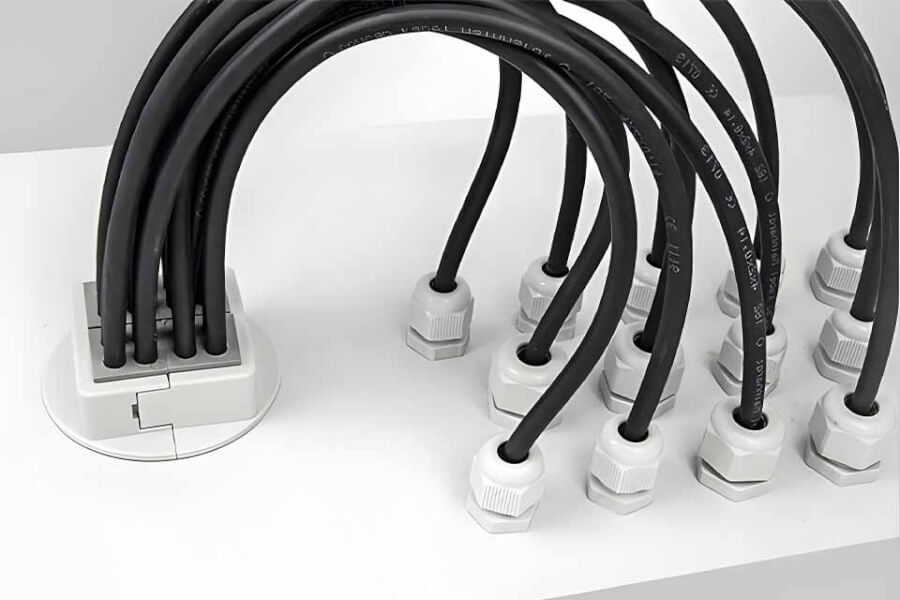
- Special types exist, like multi hole cable gland options, which allow several cables to enter through one fitting, saving space.
As a manufacturer in China, we offer this versatility. We produce:
- Plastic water proof cable gland (often nylon): Great value, good sealing, widely used.
- Metal water proof cable gland (brass, stainless steel): Very strong, excellent for grounding armor, resists corrosion.
- Multi hole cable gland: Space-saving for multiple cables.
- Along with related items like junction box solutions.
This variety means you can find the perfect fit for almost any cable type and application, ensuring a secure and reliable connection every time.
H2: Which Industries Need Cable Glands the Most?
Cable glands aren’t just used in one or two places. They are vital across many important industries. The global market for cable glands was valued around USD 1.97 Billion in 2024 and is growing, expected to reach over USD 3.1 Billion by 2033. This shows how essential they are! The demand is driven by things like building more infrastructure, growing industries, and the big push for renewable energy. Let’s look at where they are most critical:
| Industry | Why Cable Glands Are Needed Here | Market Impact / Statistics |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Problem: Risk of explosions, harsh weather offshore, corrosive chemicals. Agitate: Failure is catastrophic. Solution: Need explosion-proof cable glands (often ATEX-certified) and corrosion-resistant metal glands. | Huge user, needs highest safety standards . |
| Mining | Problem: Lots of dust, moisture, heavy vibrations, risk of flammable gas. Agitate: Equipment failure stops production; safety is paramount underground. Solution: Require robust, sealed (high IP rated), and often explosion-proof cable glands with strong strain relief. | Major use in heavy machinery and tunnels [17]. |
| Marine / Offshore | Problem: Constant exposure to saltwater, moisture, vibration. Agitate: Corrosion destroys connections quickly; reliability is key at sea. Solution: Need IP68 cable glands for marine use, usually made of brass or stainless steel to resist salt corrosion. | Specific material needs drive this segment. |
| Manufacturing & Factories | Problem: Dust, potential water splashes, vibration from machinery, need for reliable automation. Agitate: Downtime costs money; electrical noise can disrupt robots. Solution: Use durable glands with good sealing and strain relief. Metal glands help with grounding and sometimes EMI shielding for robots/automation. | Growing fast with Industry 4.0 automation. |
| Renewable Energy (Solar/Wind) | Problem: Outdoor installations face rain, sun (UV), wind, temperature changes. Agitate: Weather damage reduces energy production; reliability is crucial. Solution: Need weatherproof, UV-resistant glands (often plastic waterproof cable glands with high IP ratings) for solar panels and wind turbines. | Big growth area needing durable outdoor solutions. |
| Chemical Plants | Problem: Exposure to corrosive chemicals, potentially hazardous areas. Agitate: Chemical damage leads to failure; safety rules are strict. Solution: Require chemically resistant materials (like stainless steel) and potentially ATEX-certified cable glands. | Material choice is critical here. |
| Aerospace & Defense | Problem: Extreme conditions, need for reliability, specific standards. Agitate: Failure is not an option in planes or military gear. Solution: High-spec glands meeting strict requirements. | Demands highest quality and specific certs. |
This table shows just how widespread the need is. From deep mines to offshore platforms to modern factories, cable glands are the unsung heroes keeping electrical systems safe and reliable. As a manufacturer in China, we supply durable plastic and metal waterproof cable glands suitable for many of these industries, helping ensure their operations run smoothly.
H2: How Do I Pick the Right Cable Gland? (A Simple Guide)
Problem: There are so many types of cable glands! How do you know which one is right for your job? Picking the wrong one can lead to all the problems we want to avoid.
Agitate: Choosing incorrectly might mean the gland doesn’t seal properly, letting in water or dust. It might not grip the cable tightly, losing the strain relief. If you use a regular gland in a hazardous area, you create a huge safety risk. Using a plastic gland where a strong metal one is needed could lead to breakage. It feels confusing, and a mistake could be costly or dangerous.
Solution: Don’t worry! Choosing the right gland is easier if you follow these simple steps. Think of this as your basic cable gland selection guide:
Step 1: What Kind of Cable Do You Have?
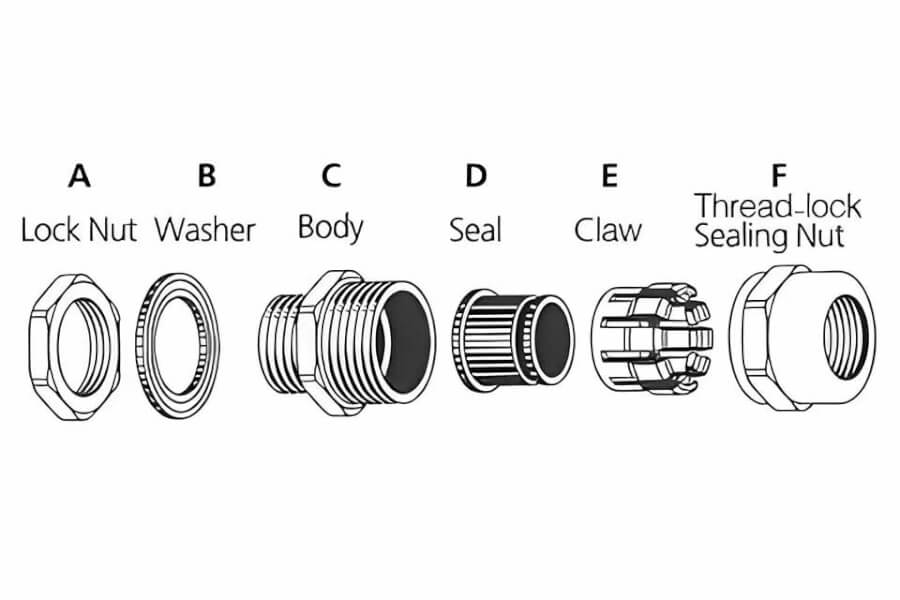
- Armored Cable? (Has a metal layer like steel wires under the outer cover). You need a gland specifically designed for armored cable. These usually have two parts to clamp: one for the inner part of the cable, and one for the armor itself to ensure grounding.
- Unarmored Cable? (Just a regular plastic-covered cable). You can use a simpler non-armored cable gland. These are very common.
Step 2: What Job Does it Need to Do? (Environment & Protection)
- Keep Water/Dust Out? Look at the IP rating.
- IP65/IP66: Good against dust and water jets (like rain or washing down).
- IP67/IP68: Better protection, can handle being submerged in water for a time. IP68 cable glands for marine use or very wet areas are best.
- Resist Chemicals or Salt? Think about the material.
- Plastic (Nylon): Good general purpose, resists many common chemicals, cost-effective. Our plastic water proof cable gland options are great for many uses.
- Brass: Strong, resists corrosion well (good near saltwater), good for grounding. Check out our metal water proof cable gland selection.
- Stainless Steel: Best for very harsh chemicals or very high temperatures, very strong, excellent corrosion resistance.
- Need Lots of Cables in One Spot? Consider a multi hole cable gland to save space.
Step 3: Is it a Dangerous (Hazardous) Area?
- Risk of Explosion (Gas/Dust)? You must use an explosion-proof cable gland with the correct certification (like ATEX-certified cable glands or IECEx). Safety first!
Step 4: What Size is Your Cable?
- Measure the diameter (how thick) your cable is. Cable glands come in many sizes (like M20, PG16, NPT 1/2″). Choose a gland where your cable diameter fits comfortably within its clamping range (the min and max size it can grip).
By thinking through these steps, you can choose the right gland for safety and reliability. As a cable gland manufacturer, we provide clear information about our products’ IP ratings, materials, and cable ranges to help you make the best choice. Whether it’s our versatile plastic glands or robust metal glands, we aim to provide the solution you need.
H2: Quick Questions About Cable Glands (FAQs)
Here are some common questions people ask:
Q: Do I really need cable glands for indoor use where it’s dry? A: Yes, often you still do! Even indoors, glands provide important strain relief, stopping cables from being pulled out or damaged by vibration. They also keep dust out of sensitive equipment, which can be important in workshops or even offices with computers. Plus, they make the entry point look neat and professional.
Q: Can I use one size of cable gland for all my different cables? A: No, that’s usually not a good idea. Each cable gland is designed for a specific range of cable diameters (thicknesses). Using a gland that’s too big won’t seal or grip properly. Using one that’s too small might damage the cable or just won’t fit. Always check the gland’s size range and match it to your cable diameter for a safe and secure fit.
Q: Are plastic cable glands okay to use in hot places? A: Standard nylon (plastic) cable glands are usually rated for temperatures up to around 80-100°C (176-212°F), which is fine for most normal applications. However, if the area gets extremely hot (like near an engine or furnace), a metal cable gland (brass or stainless steel) is usually a better choice as they can handle much higher temperatures without softening or degrading. Always check the temperature rating of the specific gland you plan to use.
H2: Conclusion: Cable Glands Are Small Parts That Do a Big Job!
So, why are cable glands used? As we’ve seen, these small but mighty devices are essential for keeping electrical systems safe, reliable, and long-lasting.
Problem Recap: Without them, cables are exposed to water, dust, and damage. Connections can fail. Wires can pull loose. In dangerous areas, the risk of fire or explosion is real. These issues lead to costly downtime, repairs, and serious safety hazards.
Agitation Recap: Ignoring proper cable entry can cause equipment breakdowns, stop production, lead to accidents, and result in non-compliance with safety standards. It’s a risk not worth taking.
Solution Recap: Cable glands solve these problems!
- They seal out the bad stuff (water, dust).
- They provide strain relief, holding cables tight.
- They ensure safety in hazardous areas.
- They help with grounding.
- They make cables last longer.
- They help you meet industry standards.
- They work with many cable types.
From giant oil & gas rigs and busy manufacturing plants to renewable solar energy farms and everyday electrical boxes, cable glands are everywhere, quietly doing their vital job.
As a dedicated cable gland manufacturer in China, we understand these needs deeply. We are proud to produce high-quality:
- Plastic water proof cable gland
- Metal water proof cable gland
- Multi hole cable gland
- And associated junction box solutions.
We focus on providing reliable, cost-effective products that give you the protection and peace of mind you need.
Need help choosing the right cable gland for your project? Explore our range or contact us today! We are here to help you find the perfect solution to keep your connections secure and your operations running safely. Visit www.cagland.com to learn more.
News & Blog
Discover what cable glands are, why they matter, and how the right choice protects cables, boosts safety, and ensures reliable performance in any environment.