Table of Contents
Stop Electrical Noise! What is an EMC Cable Gland and Why You Need It
Does bad electrical noise mess up your machines? Does it make screens flicker or computers stop? This is a big problem. It can cost you money. It can make things unsafe. This noise is called EMI, or electromagnetic interference. It’s like static on a radio, but for your important electric parts. Finding the right way to stop it can feel hard. There are so many parts and rules.
You might worry:
- Will my machines break down?
- Will I lose important data?
- Is my workplace safe from electrical problems?
- How can I fix this without spending too much?
These worries are real. Bad electrical noise is everywhere. It comes from motors, lights, radios, and even phones. If it gets into your sensitive wires, it causes trouble. Your machines might not work right. Safety systems could fail. It’s a headache you don’t need. Fixing it after it happens costs way more than stopping it first.
But there is a good solution! It’s called an EMC cable gland. EMC means Electro Magnetic Compatibility. These special parts stop the bad noise. They make sure your machines work smoothly and safely.
We are a maker of cable glands in China. We know how important it is to protect your wires. We make strong parts to help you. This guide will tell you all about EMC cable glands. You will learn what they are, how they work, and why they are so important. We want to help you solve the problem of electrical noise for good.

1. What is an EMC Cable Gland? Your Shield Against Noise
So, what exactly is an EMC cable gland?
Think of it like a special door for your electrical cables. Cables need to go into boxes or machines. A cable gland is the part that lets the cable go through the wall of the box safely.
But an EMC cable gland does more. It has a superpower: it stops bad electrical noise (EMI).
- Problem: Regular holes or simple cable glands let cables in, but they also let bad noise in. This noise travels along the cable’s metal shield and can mess up the electronics inside the box.
- Agitate: If this noise gets in, your expensive machines might stop working. You could lose time and money. In some places, like hospitals or factories, this could even be dangerous. You need a way to block that noise at the door!
- Solution: An EMC cable gland is designed to connect to the cable’s shield perfectly. It grounds the noise right where the cable enters the box. It acts like a bouncer, keeping the bad noise out and letting the good signals pass through. It keeps the shielding strong all the way from the cable into the box.
In simple terms: An EMC cable gland is a special connector for cables that does three main things:
- Lets a cable enter a box or machine.
- Holds the cable tight so it doesn’t pull out.
- Stops bad electrical noise (EMI) from getting inside by grounding the cable’s shield.
We make many types of cable glands, including strong metal water proof cable gland options that are great for tough spots. EMC glands are a key part of making sure electrical systems work right.
2. How Do EMC Cable Glands Stop the Noise? (It’s Clever!)
How can a small part do such a big job? It seems like magic, but it’s just smart design.
- Problem: Electrical noise wants to travel along the metal parts of your cables, especially the outer shield. If that shield connects poorly when entering a box, the noise just jumps inside.
- Agitate: A bad connection is like leaving the door open for noise. Even a tiny gap can let EMI in and cause chaos. You might think you are protected, but a poorly designed gland means you are still at risk. Your whole system depends on every part working perfectly.
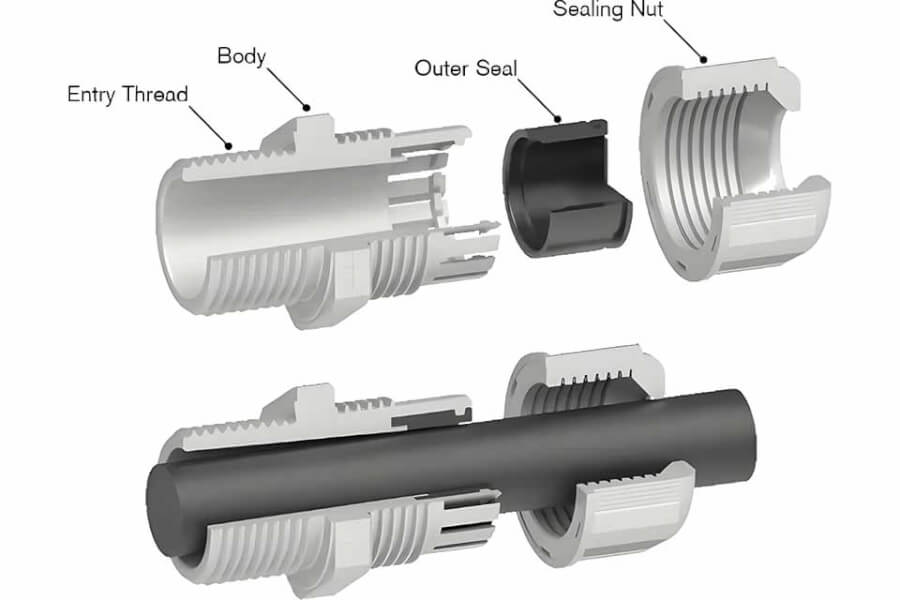
- Solution: EMC cable glands use clever tricks to make a perfect, 360-degree connection to the cable’s shield.
- Faraday Cage Idea: They help turn your metal box into a shield itself, like a Faraday cage. This cage blocks electrical fields. The gland makes sure the cable shield connects tightly to the box wall, keeping the shield strong.
- Special Inside Parts: Many EMC glands have metal fingers or springs inside. When you tighten the gland, these fingers press firmly all around the cable’s shield. This makes a solid electrical path for the noise to go safely to the ground, instead of into your machine.
- Good Materials: They are made of metal (like brass or stainless steel) that conducts electricity well. This helps the noise flow away easily.
They also do other jobs:
- Keep Water Out: Many EMC glands, like our metal water proof cable gland and plastic water proof cable gland, are also waterproof and dustproof. They have seals that squeeze the cable tight. This stops water and dirt getting inside your box (look for IP ratings like IP68).
- Hold the Cable: They grip the cable so it can’t be pulled out by accident. This is called strain relief. It stops the wires inside from breaking.
As a manufacturer, we focus on designs that make a reliable, low-resistance connection to the shield. This is key for good EMC protection.
3. Why Use EMC Cable Glands? The Big Benefits
Using the right parts makes a huge difference. Why should you choose EMC cable glands?
- Problem: Choosing electrical parts can be confusing. You need something strong, reliable, and easy to use. But many options look the same. How do you pick the best one for the job?
- Agitate: Picking the wrong part can lead to big problems later. A weak gland might break. A leaky one lets water in. A complex one wastes your valuable time during setup. Even worse, if it doesn’t stop EMI, your whole reason for using it is gone. You end up with the same noise problems you tried to avoid.
- Solution: EMC cable glands offer key benefits that solve these problems:
- Stop Noise (EMC): This is their main job! They keep your equipment safe from EMI. Peace of mind.
- Strong and Tough: Made from materials like brass (often nickel-plated) or stainless steel, they resist rust and damage. They last a long time, even in tough places. We ensure our glands use quality materials.
- Easy to Put In: Many modern EMC glands are designed to be simple and fast to install. This saves you time and money on labor. Our designs focus on being user-friendly.
- Keep Out Water and Dust: High IP ratings (like IP68) mean they give great protection against the environment. This is vital outdoors or in dirty areas. Our waterproof glands excel here.
- Safety Tested: Many EMC glands meet safety standards for use in dangerous areas (like ATEX or IECEx for places with gas or dust. This is crucial for industries like oil and gas.
Using certified, well-made EMC cable glands means you are building a reliable and safe system. It’s an investment that prevents bigger costs later.
4. What Kinds of EMC Cable Glands Are There?
Not all EMC cable glands are the same. They come in different types to fit different needs.
- Problem: With so many cables and situations, how do you know which type of EMC gland is right? Does the material matter? What about the cable itself?
- Agitate: Using the wrong type can be ineffective or even damage your cable. A gland meant for a plain cable won’t work right on an armored one. A plastic gland might not be suitable for a very harsh chemical place. This confusion can lead to mistakes and poor performance.
Solution: EMC glands can be grouped in a few ways:
By Material:
- Brass (Nickel-Plated): Very common, strong, good conductivity, resists rust. Great for general industrial use. Our metal water proof cable gland often uses this.
- Stainless Steel: Super tough, best for food processing, chemical plants, or very salty places (like near the ocean). Costs more but lasts longer in extreme conditions.
- Plastic: Lighter weight, good insulation, often lower cost. Used where metal is not needed or could cause issues. Our plastic water proof cable gland is a versatile option. Note: For EMC, plastic glands need special metal parts inside to ground the shield.
By Cable Type:
- For Normal (Unarmored) Cables: These have springs or fingers to grip the braided shield.
- For Armored Cables: These have extra parts to clamp both the inner shield (for EMC) and the outer metal armor (for grounding and holding).
By Thread Type:
- Metric (M): The most common standard worldwide (e.g., M20, M25).
- NPT: Common in North America.
- PG: An older standard, still used sometimes.
Special Types:
- Multi-Hole Glands: Some glands can seal several cables in one fitting. While less common for high-level EMC needs, our multi hole cable gland offers space-saving solutions for general sealing. EMC versions exist but are specialized.
Choosing the right type depends on your cable, your environment, and the level of protection you need. As manufacturers, we can help guide you to the best choice from our range.

5. Putting Them In Right: Installation and Care
An EMC cable gland only works well if it’s put in correctly.
- Problem: Installing electrical parts can be tricky. If you don’t do it right, it might not work, or even be unsafe. How do you make sure the EMC gland is doing its job?
- Agitate: A bad installation completely wastes the benefit of an EMC gland! The noise will still get through. You might tighten it too much and damage the cable, or too little and leave gaps for noise and water. This can lead to failures that are hard to find later. It’s frustrating and costly.
- Solution: Follow simple steps for a good installation:
- Prepare the Cable: Carefully strip the outer jacket of the cable to show the braided shield. Don’t nick the shield!
- Insert Cable: Pass the cable through the gland.
- Connect the Shield: Make sure the gland’s internal fingers or spring make good, solid contact all around the shield. This is the most important step for EMC.
- Tighten the Gland: Tighten the gland body into the box wall first. Then tighten the back nut onto the cable. Use the right amount of force (torque) – not too tight, not too loose[^6]. This creates the seal and grips the cable.
- Check: Give the cable a gentle pull to ensure it’s held firmly. Check that the gland is tight in the panel.
Care Tips:
- Check Regularly: Especially in tough places, look at the glands sometimes. Make sure they are still tight and not damaged or rusted.
- Keep Clean: Dirt buildup could affect the grounding over a long time, though good designs minimize this.
Well-designed EMC glands, like the ones we aim to make, are made for easy and reliable installation. Following the instructions is key to getting the full protection.
6. Where Are EMC Cable Glands Used? Many Industries Need Them!
EMC protection is not just a nice thing to have; it’s often needed by rules or for reliable work.
- Problem: Where is this electrical noise problem the worst? Do I need to worry about it in my specific job or industry?
- Agitate: Ignoring EMC needs can lead to big failures in critical systems. Imagine hospital equipment failing, factory robots stopping, or communication networks going down. This can have huge safety and financial costs. Regulations in many industries require proper EMC protection. Not meeting them can mean fines or shutdowns.
Solution: EMC cable glands are vital in many places where machines and electronics must work perfectly:
- Telecommunications: Data centers, cell towers – they need clean signals. EMC glands stop noise from messing up data. The U.S. telecom sector relies on good connections.
- Industrial Automation: Factories with robots, sensors, and control panels. EMC glands protect sensitive controls from noisy motors and machines.
- Oil and Gas: Drilling rigs, refineries. These are often hazardous areas needing special certified glands (ATEX/IECEx) to prevent sparks and stop EMI.
- Transportation: Trains, ships, airplanes. Lots of electronics need protection from interference.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines, solar farms. Control systems need to be reliable.
- Medical: Hospitals use sensitive electronic equipment that must be protected from interference.
- Military and Aerospace: Strict requirements for reliability and performance.
The market for EMC cable glands is growing. It was valued at USD 2.61 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 4.32 Billion by 2032. That’s a growth rate (CAGR) of 6.50% per year[^1]! Another report suggests a CAGR of 7.00%. This shows more and more industries realize how important EMC protection is.
Wherever you need reliable electrical connections safe from noise, EMC cable glands are often the answer. Our related products, like sturdy junction box solutions, also play a role in protecting connections in these industries.
7. EMC Cable Glands vs. Connectors: What’s the Difference?
Are EMC cable glands the same as electrical connectors? No, they have different jobs.
- Problem: People sometimes mix up glands and connectors. They both connect things, right? What makes them different?
- Agitate: Using a gland where you need a connector, or vice versa, can cause problems. You might not get the shielding you need, or you might not be able to easily disconnect things later. This confusion can lead to designing a system that is hard to maintain or doesn’t work right.
Solution: Let’s make it simple:
EMC Cable Gland:
- Main Job: Let a cable enter an enclosure (box) safely, provide strain relief, seal against the environment (water/dust), AND ground the cable shield for EMC protection.
- Think: A secure gateway into a box.
Connector:
- Main Job: Join two cables together, or connect a cable to a device, so that signals or power can pass through. Designed to be connected and disconnected, often many times.
- Think: A plug and socket.
Key Differences Table:
| Feature | EMC Cable Gland | Connector | |——————|————————————-|————————————-| | Main Purpose | Cable entry, sealing, shield ground | Joining/disconnecting cables/devices| | Connection | Cable to Enclosure/Box | Cable to Cable, Cable to Device | | Disconnect? | Usually permanent installation | Designed for easy disconnection | | Focus | Sealing, Grounding, Strain Relief | Signal/Power Transfer, Mating Cycles|
Both can be designed for EMC. An EMC connector will also have features to ground the shield. But their main roles are different. You use an EMC gland where a cable enters a box permanently. You use a connector where you need to plug and unplug cables.
As a manufacturer focused on secure cable entry, our core products are cable gland solutions, including metal, plastic, and multi-hole types, as well as protective junction boxes.
8. Rules and Tests: Making Sure Glands Are Safe and Effective
How do you know an EMC cable gland actually works and is safe? By checking its certifications.
- Problem: Anyone can say their product is good. How do you trust that it meets safety rules and performs as promised? Especially for something important like EMC protection.
- Agitate: Using parts that are not properly tested or certified is risky. They might fail when you need them most. They could cause safety hazards. If something goes wrong, using uncertified parts could void warranties or even lead to legal trouble. You cannot afford to take chances with safety and reliability.
Solution: Reputable manufacturers test their EMC cable glands according to international standards. Look for these marks:
- EMC Standards (like EN 61000 series): These tests check how well the gland stops electromagnetic interference. They measure its ability to ground the shield effectively (low impedance).
- IP Rating (Ingress Protection, e.g., IP68): This tells you how well it seals against dust and water. IP68 means it’s dust-tight and can go underwater. Very important for outdoor or wet locations.
- Hazardous Area Certifications (ATEX, IECEx, UL): These are crucial for glands used in places with flammable gas or dust (like oil rigs, mines, chemical plants). They prove the gland won’t cause a spark.
- Material Standards (UL, RoHS): These check the safety and environmental impact of the materials used.
When you choose EMC cable glands with the right certifications for your needs, you can be confident they will perform safely and effectively. We believe in quality and ensure our products, from basic waterproof glands to specialized solutions, are made to meet relevant industry expectations.
9. How to Pick the Right EMC Cable Gland for Your Needs
Okay, you know you need an EMC gland. Now, how do you choose the perfect one?
- Problem: There are many options – different sizes, materials, types. Picking the exact right one feels overwhelming. What should you look for?
- Agitate: Choosing wrong leads to wasted money or poor protection. You might buy a super expensive stainless steel gland when a brass one would do. Or you might pick one that doesn’t fit your cable size or thread type, causing delays and frustration. Making the wrong choice compromises the whole point – reliable EMC shielding.
Solution: Ask these simple questions:
What Type of Cable Am I Using?
- Is it shielded? (It must be for an EMC gland to work).
- Is it armored or unarmored?
- What is the outer diameter of the cable? The gland must fit this size range[^9].
Where Will It Be Used (Environment)?
- Indoors or outdoors? Needs waterproofing (IP rating)?
- Is it very hot or cold?
- Are there chemicals or salt? (Might need stainless steel).
- Is it a hazardous area (needs ATEX/IECEx)?
What Size Thread Do I Need?
- Check the hole in your box or machine. Is it Metric (M20, M25 etc.), NPT, or PG?[^9]
How Much EMC Protection Do I Need?
- For very sensitive equipment, you might need glands with proven high shielding performance (tested attenuation values). For less critical uses, a standard EMC gland may be fine.
Think about our products:
- Need strong, general-purpose EMC protection, also waterproof? Our metal water proof cable gland (EMC version) is often a great choice.
- Need a lighter, possibly lower-cost option, still waterproof? Look at plastic water proof cable gland (with EMC features).
- Need to bring multiple less critical cables into one spot? Our multi hole cable gland saves space (check if EMC versions meet your specific need).
By considering these points, you can choose the EMC cable gland that gives you the best performance, reliability, and value.
10. Conclusion: Your Best Defense Against Electrical Noise
We’ve covered a lot about EMC cable glands. Let’s wrap it up.
- Problem Recap: Electrical noise (EMI) is a silent threat. It can disrupt your machines, corrupt data, and compromise safety. Protecting against it is essential in today’s electronic world.
- Agitation Recap: Ignoring EMI is like leaving your door unlocked for trouble. Failures, downtime, safety risks – the consequences are serious and costly. You need a reliable way to lock out that noise.
- Solution Recap: EMC cable glands are the solution! They are special parts that let cables enter boxes while blocking harmful EMI by grounding the cable shield. They also provide sealing against water and dust, and hold cables securely.
Key Takeaways:
- EMC cable glands are vital for reliable operation in many industries.
- They work by making a solid connection to the cable shield.
- Choose the right type based on cable, environment, and required certifications.
- Correct installation is crucial for them to work properly.
- The market for these parts is growing fast, showing their importance.
As a cable gland manufacturer in China, we understand these challenges. We are committed to providing high-quality solutions, including:
- Reliable metal water proof cable gland options.
- Versatile plastic water proof cable gland types.
- Space-saving multi hole cable gland designs.
- Durable junction box enclosures.
We focus on quality materials, smart design for easy installation, and meeting the standards you need. Don’t let electrical noise be your weak link. Choose the right protection. Choose reliable components.
FAQ Section: Quick Answers
Q: Can I use an EMC gland on a cable without a shield?
- A: No. EMC glands work by connecting to the cable’s metal shield. If there’s no shield, the EMC function won’t work. You would just use a regular waterproof gland like our plastic water proof cable gland.
Q: Are EMC glands much more expensive than regular glands?
- A: They usually cost a bit more because they have extra conductive parts inside. But the cost is small compared to the cost of equipment failure caused by EMI.
Q: Can EMC glands replace connectors?
- A: No, they do different jobs. Glands are for fixed cable entry into boxes. Connectors are for joining cables or plugging into devices.
Q: Are EMC glands reusable?
- A: Sometimes. If you carefully remove it without damaging the gland or its seals, you might be able to reuse it. But always check it carefully before reusing. For critical uses, it’s often best to use a new one.
Q: Do I need special tools to install EMC glands?
- A: Usually just standard wrenches to tighten them. Some special types might need specific tools, but common ones are designed for standard tools.
News & Blog
Our factory offers OEM, ODM service, and custom cable glands for you. We are professionals on plastic cable glands, metal cable glands, and distribution boxes.